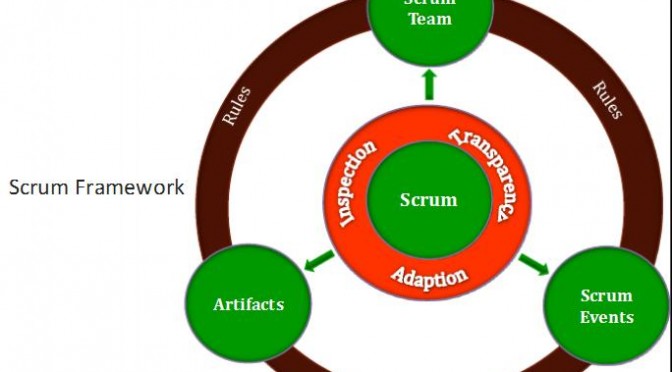
One of the most successful agile methods because of its hyper productivity
It is management oriented
Somewhat CMM Level 3 equivalence
Widely Used. Examples:
It is management oriented
Somewhat CMM Level 3 equivalence
Widely Used. Examples:
- Google Adwords
- 3M
Scrum Roles
- Scrum Master (Conducts daily scrum meeting, assure scrum rules are followed, removes obstacles, shields teams, facilitator not a manager)
- Product Owner(Accountable for product success, defines product features, maintains product backlog)
- Development team
- Other parties involved
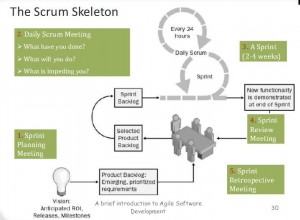
Sprint
- Time Box – 2 to 4 weeks
- An iteration for a building a piece of increment
- It’s the working time, not planning or asking what to do
- the team manages itself during a sprint
- the team commits to product backlog during sprint planning meeting
- The Sprint backlog is updated a sprint